1_[spring]response 내려주기 Restcontroller 혹은 페이지 컨트롤러, 그리고 plain text, json, html
Response 내려주기 및 모범사례
- Text로 내려주는 방법(plain text)
먼저, 가장 기본적인 형태로 String을 response로 내려주었던 것을 다시 살펴보자
Query Parameter를 인자로 받고, 받은 인자를 echo 처리해주자
package com.responseexample.responseex.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
@GetMapping("/text")
public String text(@RequestParam String account){
return account;
}
}
이 상태에서는 내가 만약에 김길동 계정을 요청한다면
http://localhost:8089/api/text?account=김길동 과 같이 조회요청을 하게 되는 것이고, 화면에는 “김길동”이라고 뜰 것이다!
- Json을 이용하여 내려주는 방법 ( 가장 많이 사용 ) - application/json
이번에는
{
"name":"이름",
"age":20,
"phone_number":"핸드폰번호",
"address":"주소"
}
위와 같은 형태의 json 데이터를 사용자가 서버로 보내고, 서버는 사용자에게 그대로 보여주는 것을 예시로 해보자!
json 데이터에 대해서 정보를 입력받고 보여주도록 하고 싶기 때문에, POST 혹은 PUT을 사용해야 하는데, POST를 이용해보도록 하자
우선 위의 형태의 dto 객체를 만드는데, naming 차이가 있기 때문에
JsonNaming을 이용해서 매칭시켜주자. 그 후에는 PostMapping 후 RequestBody를 이용해서 DataBody의 데이터를 읽어오도록 하자
package com.responseexample.responseex.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategy;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming;
@JsonNaming(value= PropertyNamingStrategy.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, String phoneNumber, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@PostMapping("/json")
public User jSon(@RequestBody User user){
return user;//echo
}
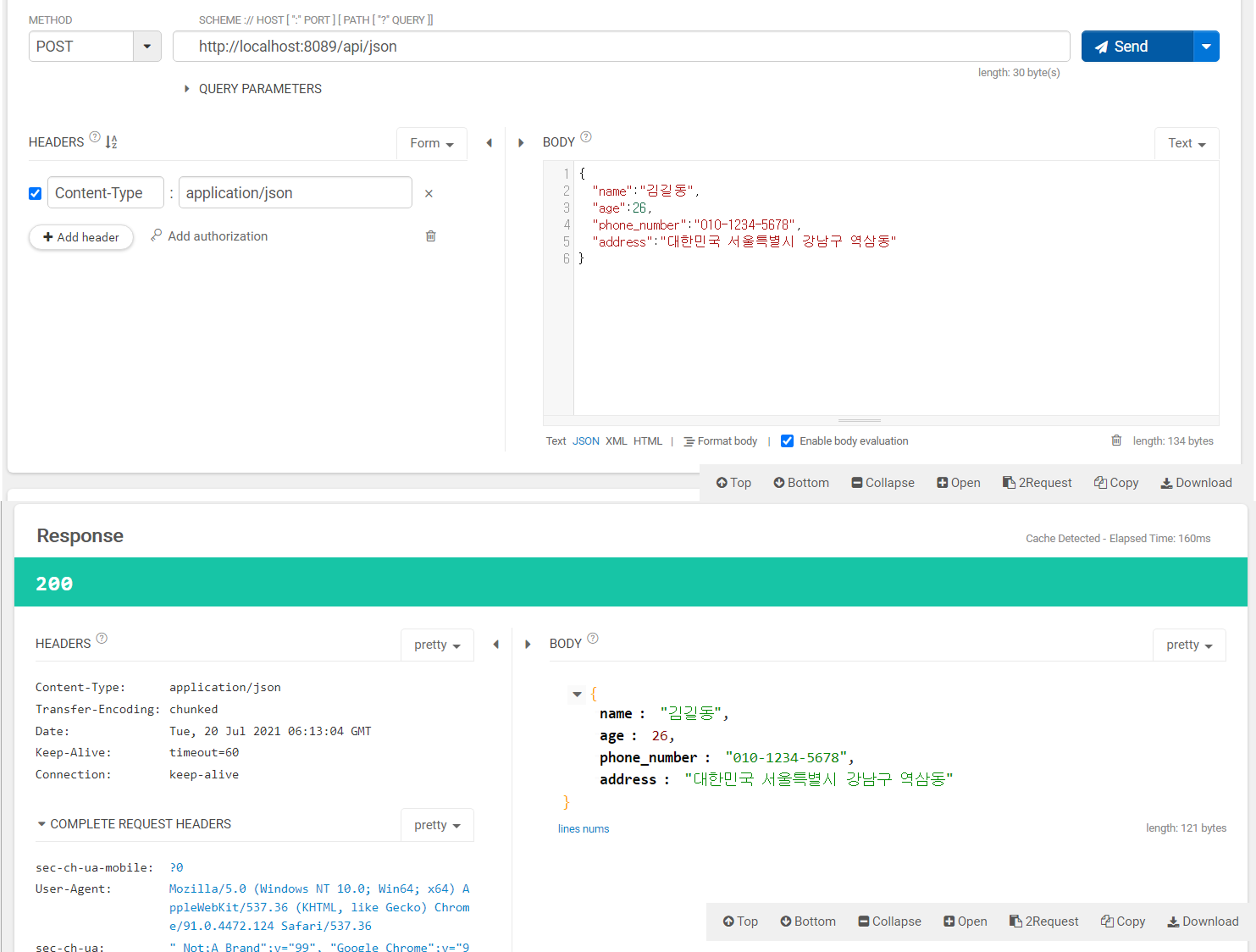
그러면 위와 같이 json형태의 데이터가 보여짐을 확인해볼 수 있다!
🌟 json객체로 response를 내려주려면,
스프링 부트에서 아래처럼
request ▶️ object mapper ▶️ object ▶️ 메서드 ▶️ object mapper ▶️ json ▶️ response
요청을 받으면 Object Mapper가 Object로 변환되고, 메서드를 통해서 Object Mapper가 json의 형태를 response로 내려주게 된다
- 가장 명확하게 응답을 내려줄 수 있는 방법 ResponseEntity의 status와 body 이용하기
- PUT(리소스 생성, 수정)은 응답이 성공되면 200,201 상태코드를 보내줄 수 있는데 201 상태에 대해서 처리해보자
@PutMapping("/put")
public ResponseEntity<User> put(@RequestBody User user){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(user);
}

먼저
- 객체를 ResponseEntity에 담는 자료형태로 반환하도록 명시해주고(ResponseEntity
) - ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.상태).body(데이터 바디에 실어줄 데이터)
를 반환해주는 것이다!
참고로, ctrl+HttpStatus 클릭을 진행하면
/*
* Copyright 2002-2021 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.http;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Enumeration of HTTP status codes.
*
* <p>The HTTP status code series can be retrieved via {@link #series()}.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Sebastien Deleuze
* @author Brian Clozel
* @since 3.0
* @see HttpStatus.Series
* @see <a href="https://www.iana.org/assignments/http-status-codes">HTTP Status Code Registry</a>
* @see <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_HTTP_status_codes">List of HTTP status codes - Wikipedia</a>
*/
public enum HttpStatus {
// 1xx Informational
/**
* {@code 100 Continue}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.2.1">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.2.1</a>
*/
CONTINUE(100, Series.INFORMATIONAL, "Continue"),
/**
* {@code 101 Switching Protocols}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.2.2">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.2.2</a>
*/
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS(101, Series.INFORMATIONAL, "Switching Protocols"),
/**
* {@code 102 Processing}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2518#section-10.1">WebDAV</a>
*/
PROCESSING(102, Series.INFORMATIONAL, "Processing"),
/**
* {@code 103 Checkpoint}.
* @see <a href="https://code.google.com/p/gears/wiki/ResumableHttpRequestsProposal">A proposal for supporting
* resumable POST/PUT HTTP requests in HTTP/1.0</a>
*/
CHECKPOINT(103, Series.INFORMATIONAL, "Checkpoint"),
// 2xx Success
/**
* {@code 200 OK}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.1">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.1</a>
*/
OK(200, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "OK"),
/**
* {@code 201 Created}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.2">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.2</a>
*/
CREATED(201, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Created"),
/**
* {@code 202 Accepted}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.3">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.3</a>
*/
ACCEPTED(202, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Accepted"),
/**
* {@code 203 Non-Authoritative Information}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.4">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.4</a>
*/
NON_AUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION(203, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Non-Authoritative Information"),
/**
* {@code 204 No Content}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.5">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.5</a>
*/
NO_CONTENT(204, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "No Content"),
/**
* {@code 205 Reset Content}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.3.6">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.3.6</a>
*/
RESET_CONTENT(205, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Reset Content"),
/**
* {@code 206 Partial Content}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-4.1">HTTP/1.1: Range Requests, section 4.1</a>
*/
PARTIAL_CONTENT(206, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Partial Content"),
/**
* {@code 207 Multi-Status}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4918#section-13">WebDAV</a>
*/
MULTI_STATUS(207, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Multi-Status"),
/**
* {@code 208 Already Reported}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5842#section-7.1">WebDAV Binding Extensions</a>
*/
ALREADY_REPORTED(208, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "Already Reported"),
/**
* {@code 226 IM Used}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3229#section-10.4.1">Delta encoding in HTTP</a>
*/
IM_USED(226, Series.SUCCESSFUL, "IM Used"),
// 3xx Redirection
/**
* {@code 300 Multiple Choices}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.1">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.1</a>
*/
MULTIPLE_CHOICES(300, Series.REDIRECTION, "Multiple Choices"),
/**
* {@code 301 Moved Permanently}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.2">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.2</a>
*/
MOVED_PERMANENTLY(301, Series.REDIRECTION, "Moved Permanently"),
/**
* {@code 302 Found}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.3">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.3</a>
*/
FOUND(302, Series.REDIRECTION, "Found"),
/**
* {@code 302 Moved Temporarily}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1945#section-9.3">HTTP/1.0, section 9.3</a>
* @deprecated in favor of {@link #FOUND} which will be returned from {@code HttpStatus.valueOf(302)}
*/
@Deprecated
MOVED_TEMPORARILY(302, Series.REDIRECTION, "Moved Temporarily"),
/**
* {@code 303 See Other}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.4">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.4</a>
*/
SEE_OTHER(303, Series.REDIRECTION, "See Other"),
/**
* {@code 304 Not Modified}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-4.1">HTTP/1.1: Conditional Requests, section 4.1</a>
*/
NOT_MODIFIED(304, Series.REDIRECTION, "Not Modified"),
/**
* {@code 305 Use Proxy}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.5">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.5</a>
* @deprecated due to security concerns regarding in-band configuration of a proxy
*/
@Deprecated
USE_PROXY(305, Series.REDIRECTION, "Use Proxy"),
/**
* {@code 307 Temporary Redirect}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.4.7">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.4.7</a>
*/
TEMPORARY_REDIRECT(307, Series.REDIRECTION, "Temporary Redirect"),
/**
* {@code 308 Permanent Redirect}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7238">RFC 7238</a>
*/
PERMANENT_REDIRECT(308, Series.REDIRECTION, "Permanent Redirect"),
// --- 4xx Client Error ---
/**
* {@code 400 Bad Request}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.1</a>
*/
BAD_REQUEST(400, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Bad Request"),
/**
* {@code 401 Unauthorized}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.1">HTTP/1.1: Authentication, section 3.1</a>
*/
UNAUTHORIZED(401, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Unauthorized"),
/**
* {@code 402 Payment Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.2">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.2</a>
*/
PAYMENT_REQUIRED(402, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Payment Required"),
/**
* {@code 403 Forbidden}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.3">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.3</a>
*/
FORBIDDEN(403, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Forbidden"),
/**
* {@code 404 Not Found}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.4</a>
*/
NOT_FOUND(404, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Not Found"),
/**
* {@code 405 Method Not Allowed}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.5">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.5</a>
*/
METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED(405, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Method Not Allowed"),
/**
* {@code 406 Not Acceptable}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.6">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.6</a>
*/
NOT_ACCEPTABLE(406, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Not Acceptable"),
/**
* {@code 407 Proxy Authentication Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-3.2">HTTP/1.1: Authentication, section 3.2</a>
*/
PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED(407, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Proxy Authentication Required"),
/**
* {@code 408 Request Timeout}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.7">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.7</a>
*/
REQUEST_TIMEOUT(408, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Request Timeout"),
/**
* {@code 409 Conflict}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.8">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.8</a>
*/
CONFLICT(409, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Conflict"),
/**
* {@code 410 Gone}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.9">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.9</a>
*/
GONE(410, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Gone"),
/**
* {@code 411 Length Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.10">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.10</a>
*/
LENGTH_REQUIRED(411, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Length Required"),
/**
* {@code 412 Precondition failed}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-4.2">
* HTTP/1.1: Conditional Requests, section 4.2</a>
*/
PRECONDITION_FAILED(412, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Precondition Failed"),
/**
* {@code 413 Payload Too Large}.
* @since 4.1
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.11">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.11</a>
*/
PAYLOAD_TOO_LARGE(413, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Payload Too Large"),
/**
* {@code 413 Request Entity Too Large}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-10.4.14">HTTP/1.1, section 10.4.14</a>
* @deprecated in favor of {@link #PAYLOAD_TOO_LARGE} which will be
* returned from {@code HttpStatus.valueOf(413)}
*/
@Deprecated
REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE(413, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Request Entity Too Large"),
/**
* {@code 414 URI Too Long}.
* @since 4.1
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.12">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.12</a>
*/
URI_TOO_LONG(414, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "URI Too Long"),
/**
* {@code 414 Request-URI Too Long}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616#section-10.4.15">HTTP/1.1, section 10.4.15</a>
* @deprecated in favor of {@link #URI_TOO_LONG} which will be returned from {@code HttpStatus.valueOf(414)}
*/
@Deprecated
REQUEST_URI_TOO_LONG(414, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Request-URI Too Long"),
/**
* {@code 415 Unsupported Media Type}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.13">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.13</a>
*/
UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE(415, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Unsupported Media Type"),
/**
* {@code 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-4.4">HTTP/1.1: Range Requests, section 4.4</a>
*/
REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE(416, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Requested range not satisfiable"),
/**
* {@code 417 Expectation Failed}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.14">
* HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.5.14</a>
*/
EXPECTATION_FAILED(417, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Expectation Failed"),
/**
* {@code 418 I'm a teapot}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2324#section-2.3.2">HTCPCP/1.0</a>
*/
I_AM_A_TEAPOT(418, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "I'm a teapot"),
/**
* @deprecated See
* <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/rfcdiff?difftype=--hwdiff&url2=draft-ietf-webdav-protocol-06.txt">
* WebDAV Draft Changes</a>
*/
@Deprecated
INSUFFICIENT_SPACE_ON_RESOURCE(419, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Insufficient Space On Resource"),
/**
* @deprecated See
* <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/rfcdiff?difftype=--hwdiff&url2=draft-ietf-webdav-protocol-06.txt">
* WebDAV Draft Changes</a>
*/
@Deprecated
METHOD_FAILURE(420, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Method Failure"),
/**
* @deprecated
* See <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/rfcdiff?difftype=--hwdiff&url2=draft-ietf-webdav-protocol-06.txt">
* WebDAV Draft Changes</a>
*/
@Deprecated
DESTINATION_LOCKED(421, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Destination Locked"),
/**
* {@code 422 Unprocessable Entity}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4918#section-11.2">WebDAV</a>
*/
UNPROCESSABLE_ENTITY(422, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Unprocessable Entity"),
/**
* {@code 423 Locked}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4918#section-11.3">WebDAV</a>
*/
LOCKED(423, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Locked"),
/**
* {@code 424 Failed Dependency}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4918#section-11.4">WebDAV</a>
*/
FAILED_DEPENDENCY(424, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Failed Dependency"),
/**
* {@code 425 Too Early}.
* @since 5.2
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8470">RFC 8470</a>
*/
TOO_EARLY(425, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Too Early"),
/**
* {@code 426 Upgrade Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2817#section-6">Upgrading to TLS Within HTTP/1.1</a>
*/
UPGRADE_REQUIRED(426, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Upgrade Required"),
/**
* {@code 428 Precondition Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6585#section-3">Additional HTTP Status Codes</a>
*/
PRECONDITION_REQUIRED(428, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Precondition Required"),
/**
* {@code 429 Too Many Requests}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6585#section-4">Additional HTTP Status Codes</a>
*/
TOO_MANY_REQUESTS(429, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Too Many Requests"),
/**
* {@code 431 Request Header Fields Too Large}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6585#section-5">Additional HTTP Status Codes</a>
*/
REQUEST_HEADER_FIELDS_TOO_LARGE(431, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Request Header Fields Too Large"),
/**
* {@code 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-legally-restricted-status-04">
* An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles</a>
* @since 4.3
*/
UNAVAILABLE_FOR_LEGAL_REASONS(451, Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "Unavailable For Legal Reasons"),
// --- 5xx Server Error ---
/**
* {@code 500 Internal Server Error}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.1">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.1</a>
*/
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Internal Server Error"),
/**
* {@code 501 Not Implemented}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.2">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.2</a>
*/
NOT_IMPLEMENTED(501, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Not Implemented"),
/**
* {@code 502 Bad Gateway}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.3">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.3</a>
*/
BAD_GATEWAY(502, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Bad Gateway"),
/**
* {@code 503 Service Unavailable}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.4">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.4</a>
*/
SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE(503, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Service Unavailable"),
/**
* {@code 504 Gateway Timeout}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.5">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.5</a>
*/
GATEWAY_TIMEOUT(504, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Gateway Timeout"),
/**
* {@code 505 HTTP Version Not Supported}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.6.6">HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content, section 6.6.6</a>
*/
HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED(505, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "HTTP Version not supported"),
/**
* {@code 506 Variant Also Negotiates}
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2295#section-8.1">Transparent Content Negotiation</a>
*/
VARIANT_ALSO_NEGOTIATES(506, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Variant Also Negotiates"),
/**
* {@code 507 Insufficient Storage}
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4918#section-11.5">WebDAV</a>
*/
INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE(507, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Insufficient Storage"),
/**
* {@code 508 Loop Detected}
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5842#section-7.2">WebDAV Binding Extensions</a>
*/
LOOP_DETECTED(508, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Loop Detected"),
/**
* {@code 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded}
*/
BANDWIDTH_LIMIT_EXCEEDED(509, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded"),
/**
* {@code 510 Not Extended}
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2774#section-7">HTTP Extension Framework</a>
*/
NOT_EXTENDED(510, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Not Extended"),
/**
* {@code 511 Network Authentication Required}.
* @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6585#section-6">Additional HTTP Status Codes</a>
*/
NETWORK_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED(511, Series.SERVER_ERROR, "Network Authentication Required");
private static final HttpStatus[] VALUES;
static {
VALUES = values();
}
private final int value;
private final Series series;
private final String reasonPhrase;
HttpStatus(int value, Series series, String reasonPhrase) {
this.value = value;
this.series = series;
this.reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase;
}
/**
* Return the integer value of this status code.
*/
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
/**
* Return the HTTP status series of this status code.
* @see HttpStatus.Series
*/
public Series series() {
return this.series;
}
/**
* Return the reason phrase of this status code.
*/
public String getReasonPhrase() {
return this.reasonPhrase;
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#INFORMATIONAL}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #series()
*/
public boolean is1xxInformational() {
return (series() == Series.INFORMATIONAL);
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#SUCCESSFUL}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #series()
*/
public boolean is2xxSuccessful() {
return (series() == Series.SUCCESSFUL);
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#REDIRECTION}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #series()
*/
public boolean is3xxRedirection() {
return (series() == Series.REDIRECTION);
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#CLIENT_ERROR}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #series()
*/
public boolean is4xxClientError() {
return (series() == Series.CLIENT_ERROR);
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#SERVER_ERROR}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 4.0
* @see #series()
*/
public boolean is5xxServerError() {
return (series() == Series.SERVER_ERROR);
}
/**
* Whether this status code is in the HTTP series
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#CLIENT_ERROR} or
* {@link org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series#SERVER_ERROR}.
* <p>This is a shortcut for checking the value of {@link #series()}.
* @since 5.0
* @see #is4xxClientError()
* @see #is5xxServerError()
*/
public boolean isError() {
return (is4xxClientError() || is5xxServerError());
}
/**
* Return a string representation of this status code.
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.value + " " + name();
}
/**
* Return the {@code HttpStatus} enum constant with the specified numeric value.
* @param statusCode the numeric value of the enum to be returned
* @return the enum constant with the specified numeric value
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if this enum has no constant for the specified numeric value
*/
public static HttpStatus valueOf(int statusCode) {
HttpStatus status = resolve(statusCode);
if (status == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No matching constant for [" + statusCode + "]");
}
return status;
}
/**
* Resolve the given status code to an {@code HttpStatus}, if possible.
* @param statusCode the HTTP status code (potentially non-standard)
* @return the corresponding {@code HttpStatus}, or {@code null} if not found
* @since 5.0
*/
@Nullable
public static HttpStatus resolve(int statusCode) {
// Use cached VALUES instead of values() to prevent array allocation.
for (HttpStatus status : VALUES) {
if (status.value == statusCode) {
return status;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Enumeration of HTTP status series.
* <p>Retrievable via {@link HttpStatus#series()}.
*/
public enum Series {
INFORMATIONAL(1),
SUCCESSFUL(2),
REDIRECTION(3),
CLIENT_ERROR(4),
SERVER_ERROR(5);
private final int value;
Series(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* Return the integer value of this status series. Ranges from 1 to 5.
*/
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
/**
* Return the {@code Series} enum constant for the supplied {@code HttpStatus}.
* @param status a standard HTTP status enum constant
* @return the {@code Series} enum constant for the supplied {@code HttpStatus}
* @deprecated as of 5.3, in favor of invoking {@link HttpStatus#series()} directly
*/
@Deprecated
public static Series valueOf(HttpStatus status) {
return status.series;
}
/**
* Return the {@code Series} enum constant for the supplied status code.
* @param statusCode the HTTP status code (potentially non-standard)
* @return the {@code Series} enum constant for the supplied status code
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if this enum has no corresponding constant
*/
public static Series valueOf(int statusCode) {
Series series = resolve(statusCode);
if (series == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No matching constant for [" + statusCode + "]");
}
return series;
}
/**
* Resolve the given status code to an {@code HttpStatus.Series}, if possible.
* @param statusCode the HTTP status code (potentially non-standard)
* @return the corresponding {@code Series}, or {@code null} if not found
* @since 5.1.3
*/
@Nullable
public static Series resolve(int statusCode) {
int seriesCode = statusCode / 100;
for (Series series : values()) {
if (series.value == seriesCode) {
return series;
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
위와 같은 상태를 확인해볼 수 있는데, 201은 CREATED임을 알 수 있다
지금 위에서 status()를 사용하였지만 ok()를 사용해도 무방할 것이다
🌟 ResponseEntity는 헤더 속성 및 그 값을 설정하는 데에 지원해줄 수도 있다!
- [HTML 형태로 응답] HTML 형태의 문서로 응답해주는 컨트롤러인 PageController를 이용
(어노테이션으로 Controller를 이용)
다음과 같이 main.html을 반환할 수 있도록 해주는 동작을 테스트해볼 것인데, RestController와 다르게 클래스 윗부분에 RequestMapping을 선언하지 않고, 메서드 위에 RequestMapping을 기입해주도록 한다
package com.responseexample.responseex.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class PageController {
@RequestMapping("/main")
public String main(){
return "main.html";
}
}
그리고, resources 폴더 내부의 static 폴더에 main.html을 아래와 같이 생성해주자
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>main</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Html Spring Boot</p>
</body>
</html>
그리고 http://localhost:8089/main 으로 응답을 받아보면
response를 html로 내려주기
위와 같이 html에서 작성했던 내용이 화면에 보이게 된다
그리고 talend에서도 응답을 잘 받은 것으로 보인다!
- 페이지를 반환해주는 pageController에서 json을 반환해주기
5-1. ResponseBody 이용
- Controller 어노테이션은 ResponseBody 어노테이션이 뒤를 이으면, 객체를 반환할 때 리소스를 찾지 않고 Response Body를 통해서 내려줌
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/user")
public User user(){
User user = new User();
//java 11에서는 var user로 사용가능(타입추론)
user.setName("steve");
user.setAddress("패스트캠퍼스");
user.setAge(20);
user.setPhoneNumber("010-1234-5678");
return user;
}
🌟 java 11에서는 마치 자바스크립트같이 var 변수~를 지원해준다고 한다. 찾아보니, 자바스크립트보다 조금 더 엄격한 방식인 것 같다! 자바스크립트에서는 정수형인지 등 까지가 아닌 number 등에 대한 구별만 하기 때문이라고 생각했다!(긴 이름의 클래스를 사용할 때에는 도움이 될 수 있다!)
본론으로 돌아와서 위의 결과를 확인해보기 위해서 http://localhost:8089/user 를 확인해보면
그러면 위와 같이 json 형태의 데이터를 talend와 브라우저에서 모두 확인해볼 수 있다
📌 ObjectMapper는 getter 메서드를 보기 때문에 자료형을 일치시켜주어야 한다!
📌 String 및 Wrapper 클래스는 값을 지정하지 않으면 null을, int는 0을 반환!
🌟 null값을 제외시킬 수 있도록 지원해주는 어노테이션 🌟
- JsonInclude를 이용하면 그 외의 경우는 배제되기 마련!
- 이외에도 NON_EMPTY 등이 존재
@JsonInclude(Include.NON_NULL)
먼저 dto를 위와 같이 변경해주고
package com.responseexample.responseex.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategy;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming;
@JsonNaming(PropertyNamingStrategy.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
@JsonInclude(value= JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, String phoneNumber, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
dto의 필드 중 String 형태를 갖는 phone number를 주석처리해주자
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/user")
public User user(){
User user = new User();
//java 11에서는 var user로 사용가능(타입추론)
user.setName("steve");
user.setAddress("패스트캠퍼스");
user.setAge(20);
// user.setPhoneNumber("010-1234-5678");
return user;
}
서버를 재시작해서 확인해보자
그러면, 원래라면 “phone_number”: “null”로 표시되었어야 하는데
null이 아닌 값들만 취급되어 아래처럼 phone number는 배제되게 된다!
이렇게 null에 대한 처리는 규격서에 정의해주고, 이에 맞게 개발해주면 된다!
보통은 “@JsonInclude(value= JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)”을 기본적으로 진행
하지만 보통은 rest api controller를 이용해서 json을 받도록 한다!
굳이 ResponseBody를 설정하지 않아도 객체를 반환해주거나
ResponseEntity를 이용해서 json 객체를 내려줄 수 있다!
5-2. ResponseEntity 이용
이 방법은 위에서 RestController와 동일하니 한번 확인만 하고 넘어가자
@PutMapping("/user02")
public ResponseEntity<User> json(@RequestBody User user){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(user);
}
그리고 get mapping을 해주게 되면, 생성하는 개념이 아니고 조회 개념이기 때문에 snake case로 요청을 보내면 인식을 할 수가 없다
따라서 camel case로 조회 요청을 보내면 응답에서는 json형태에서 phone_number로 확인가능하다!
이는 저번에 고민했던 부분 중 “get mapping 시 notation 인식 문제”와 관련되어 있어서 생각해볼 필요가 있었다!
@GetMapping("/user03")
public ResponseEntity<User> getJson(User user){
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(user);
}