1_[algorithm]기본정렬 버블정렬
버블 정렬 Bubble Sort
- (오름차순 정렬시)인접한 두 데이터를 비교해서, 앞에 있는 데이터가 뒤에 있는 데이터보다 크면, 자리를 바꾸는 정렬 알고리즘 -내림차순시, 앞의 데이터보다 뒤의 데이터가 더 크도록 바꿔주기
https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
source: https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
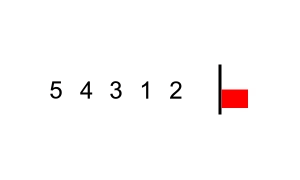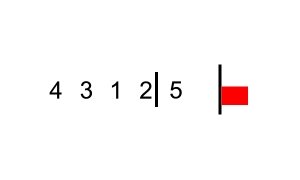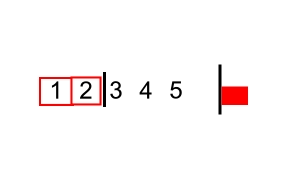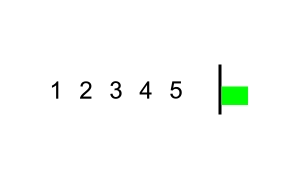
source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bubble_sort_with_flag.gif
이러한 버블 정렬을 잘 보면, 다음과 같은 특이점이 존재한다
- 크기가 n인 배열이 있다면 최대 n-1번의 로직을 적용
- 로직을 1번 적용할 때마다 가장 큰 숫자가 뒤에서 1개씩 결정됨
- 로직이 경우에 따라 일찍 끝날 수 있기 때문에, 한 번도 데이터가 교환된 적이 없다면 이미 정렬된 상태이므로 더이상 로직을 반복 적용할 필요가 없다!
그러면 아래와 같이 정리해볼 수 있다!
package sorting.bubbleSort;
public class BubbleSortTemplate {
public Integer[] BubbleSort(Integer[] arr){
Integer[] res = arr.clone();
int size = res.length;
//전체 순회 횟수
for(int i = 0 ; i < size-1; i++){
boolean swap =false;
//2개씩 비교
for(int j = 0 ; j < size-1-i;j++){
int temp = 0;
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
temp = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
swap=true;
}
}
if(swap==false){
break;
}
}
return res;
}
}
실제로 테스트를 해보면, 아래와 같이 오름차순으로 잘 정렬되는 것을 확인해볼 수 있다
package sorting.bubbleSort;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSortTemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer[] arr= new Integer[10];
BubbleSortTemplate template= new BubbleSortTemplate();
for(int i =0 ; i < 10; i++){
arr[i]=(int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
}
Integer[] res = null;
res = template.BubbleSort(arr);//[1, 47, 52, 57, 57, 72, 73, 87, 93, 99]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
🌟 알고리즘 분석 🌟
- 반복문이 두 개 ▶️O(n^2)
- 최악의 경우 (n*(n-1))/2
- 완전 정렬이 되어 있는 상태라면, 최선은 O(n)